Refrigerant Recovery
Reeders Provides Safe Disposal of Refrigerated Household Appliances.
Appliance owners play a critical role in helping to protect against environmental hazards associated with appliance disposal. The sections below provides consumers with information on:
- Environmental Concerns
- How to Dispose of an Appliance
I. Environmental Concerns
What are the environmental concerns associated with the disposal of refrigerated household appliances?
Refrigerant: Household refrigerators and freezers manufactured before 1995 typically contain chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) refrigerant. Most window air-conditioning units and dehumidifiers contain hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HCFC) refrigerant. CFCs and HCFCs are ozone-depleting substances (ODS) that, if released to the environment, destroy the protective ozone layer above the earth. Moreover, CFC and HCFC refrigerants are also potent greenhouse gases, meaning that their release contributes to global climate change. Refrigerators and freezers manufactured since 1995 contain ozone-friendly hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerants; however, these refrigerants still need to be carefully handled since they are greenhouse gases.
Foam: Refrigerators and freezers manufactured before 2005 are insulated with foam that contains ODS—either CFCs or HCFCs. If emitted, CFCs and HCFCs contribute to both ozone depletion and climate change. Only units manufactured since 2005 contain foam blowing agents that are ozone and climate friendly. Air-conditioners and dehumidifiers do not contain foam.
What are the Dangers of Used Oil, Mercury, and PCBs?
- If improperly disposed, used oil from refrigerated appliances can result in the release of dissolved ODS refrigerant and groundwater contamination. In addition, short-term exposure to used oil can cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritation; in the long-term, it can cause cancer and damage to the liver, brain, immune system, and reproductive system.
- When released to the environment, mercury accumulates in the tissues of plants and animals and, when consumed by humans, impairs neurological development and causes other problems associated with the nervous system.
- PCBs are toxic substances with carcinogenic and non-cancerous effects on humans, including effects on the immune system, reproductive system, nervous system, and endocrine system.
Hazardous Components: Household appliances may also contain hazardous components, including used oil, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and mercury. For example, the cooling circuit contains oil that can be contaminated with ODS refrigerant. Some refrigerators and chest freezers manufactured prior to 2000 have mercury-containing components (i.e., switches and relays). Appliances manufactured prior to 1979 may contain PCB capacitors. For this reason, appliances should be recycled by facilities that safely remove these components prior to shredding and recycling. The Association of Home Appliance Manufacturers (AHAM) has more information on mercury and PCBs contained in home appliances.
The diagram below provides approximate quantities and locations of substances contained in refrigerators manufactured prior to 1995.
Components of a Refrigerator Manufactured Prior to 1995
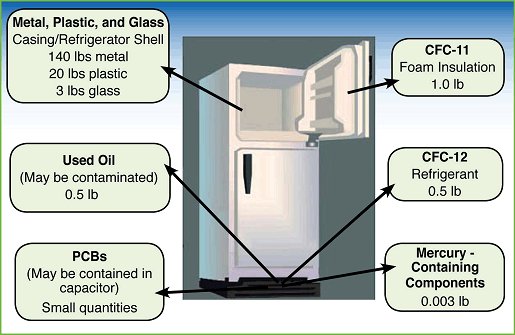
II. How to Dispose of an Appliance
How can I dispose of my refrigerated appliance in an environmentally responsible way?
First, you should check with your electric utility to see if a bounty program is offered in your area. Since some bounty programs have required specifications for appliances (e.g., must be in working condition, of a minimum vintage and/or dimension), you may also need to confirm that your appliance is acceptable. If a bounty program is not available, you can contact your municipal department of public works to inquire about the procedures for collecting and disposing of refrigerated appliances in your neighborhood. Typically, for refrigerators/freezers, municipalities require you to make an appointment for bulky item collection, which may be provided at no additional cost. Some municipalities charge a fee for refrigerated appliance collection or require you to haul items to a transfer station or dump. (Your municipality can direct you to a solid waste contractor for more information.) Other municipalities may require the refrigerant to be recovered from appliances before they will accept it for pick-up. In such cases owners would need to hire a technician with certified recovery equipment to remove the refrigerant prior to disposal.
| ! | NOTE: Do not attempt to remove refrigerant or compressors yourself. Improperly handled refrigerant may result in physical harm. Only properly trained individuals using EPA-approved refrigerant recovery equipment should attempt to remove refrigerant from appliances. |
Additional information on recycling and proper household hazardous waste disposal in your community may also be available at http://www.earth911.org/ .
Source: United States Government – EPA